LED TV Terms

LED TV Terms: a reader asked…
What’s the difference between QLED and OLED?
The first term QLED refers to a type of screen display technology used by Samsung televisions. Short for “Quantum Dot LED”, this is similar to standard LED televisions except it purports to have brighter colors. All standard LED TVs have a backlight that illuminates the colored dots on the screen, so standard LED TVs are often brighter near the edges. This technology has been around quite a while.
The term OLED (e.g., “Organic LED”) is a newer technology that requires no backlight – the dots themselves emit light. OLED is a brand-agnostic type of technology, used in many different brands of TVs. As a result, OLED TVs have deeper blacks than backlit LED TVS (including Samsung’s QLED). OLED TVs also use less power, since there’s no need for a backlight. There may be size limitations on OLED, last check showed they max out at an 88″ TV, whereas LED TVs can go much bigger.
So real world, what’s the difference? Personally, I wouldn’t pay a premium for QLED but would for OLED. I think that while the technologies are different, your viewing experience will probably not be hugely impacted. If you are outfitting a home theater experience and want the best screen available, can live with 88″ or smaller, and aren’t overly cost-conscious, then OLED is going to be your choice.
If you simply want a big screen TV at the lowest cost, go with any LED TV (including the Samsung QLED if you want). This is great for family rooms, bedrooms and other places where you don’t need a high-quality home theater experience.
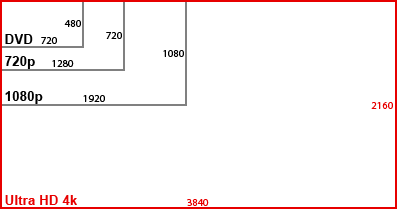
You didn’t ask, but I should mention that screen resolution is another factor. Standard DVDs offer up resolution at 720×480 pixels, while higher-quality HD TVs offer up either 1280×720 or 1092×1080 pixels. 4k HD gives you either 3840 x 2160 pixels or 4096 x 2160 pixels. I should mention that for screen sizes 40″ and smaller, you really won’t see any difference between 720 and 1080 resolution levels.
Other terms to consider include “refresh rate”, which refers to how fast the pixels on-screen refresh themselves. Slow refresh rates (e.g., 60hz where each pixel refreshes 60 times per second) may look a bit smeared when showing fast motion. Faster refresh rates (e.g., 120 or 240hz) are better for a good home theater experience or if you want to do video gaming on the big screen.
Lastly, LED TVs surpassed the older LCD technology, which was one of the first flat-screen replacements for standard cathode-ray TV tubes. Also plasma TVs came out about then, which actually offer a bit better picture than LED/LCD, but have a serious drawback – screen burn-in.
This website runs on a patronage model. If you find my answers of value, please consider supporting me by sending any dollar amount via:
or by mailing a check/cash to PosiTek.net LLC 1934 Old Gallows Road, Suite 350, Tysons Corner VA 22182. I am not a non-profit, but your support helps me to continue delivering advice and consumer technology support to the public. Thanks!